1 Creation of the Executables
2 Creation of Atomic Data Files
2.1 Level Names (TMAP Code)
2.2 List of Keywords for the Atomic Data File
2.3 Description of the Keywords
2.4 TMAD
2.4.1 Model calculations (PRO2)
2.4.2 Line-formation calculations (PRO2)
2.4.3 Spectra calculations (LINE1_PROF)
2.5 ATOMS2
2.6 TIRO
2.7 Auxiliary Programs
2.7.1 FORMEL4
2.7.2 LEVEL
2.7.3 MKIDENT_FROM_KURUCZ
2.7.4 MULTIPLET
2.7.5 SEATON
2.7.6 SGF
3 Creation of Frequency Grids
4 Start Models
4.1 PRO2 and LINE1 Models
4.2 “LTE” Models
4.3 Calculation of a LTE2 Model
4.3.1 The Method
4.3.2 The Options
5 NLTE Models: PRO2
5.1 The Method
5.2 The PARAMETERs
5.3 Input and Output Files
5.4 Input Options
5.5 Output Options
5.5.1 Output to STDOUT
5.5.2 Output into Plot Data Files
6 Adjust the log m Intervals of Existing Models: CUTM and NDSCALE
6.1 Adjust log m Intervals of Models
6.1.1 Reduce the Depth Interval: CUTM
6.1.2 Extend a Model Atmosphere to the Outside: EXTEND
6.1.3 Interpolate Models for a New Depth-Point Number: NDSCALE
7 Interpolate between Existing Models: INTER
7.1 Interpolate between Existing Models
8 NLTE Line Formation and Models: LINE1
8.1 Input Files
8.2 Output Files
8.3 Options
9 Synthetic Spectra: LINE1_PROF
10 Clean Up
10.1 Delete TMAP Working Directories
10.2 Kill TMAP Jobs
11 Auxiliaries
11.1 PLADD
11.2 PROF1
11.2.1 Line Profile Data Files
11.2.2 Spectra
11.2.3 PROF1 Auxiliary Files
11.3 PLXY
11.3.1 Keywords for Commands in Plot Data Files
11.3.2 Output devices
11.4 RTFZ
11.5 TEUV
11.6 WRPLOT
A Formula Collection
A.1 CBB Transitions
A.1.1 van-Regemorter Formula (Allowed Dipole Transitions)
A.1.2 Forbidden Transitions
A.1.3 Hydrogen
A.1.4 He IV
A.1.5 He II: Allowed Transitions from its Ground State
A.1.6 He I: Allowed Transitions but not from its Ground State
A.1.7 He I: Forbidden Transitions from its Ground State
A.1.8 He I: Forbidden Transitions between its n = 2 Sublevels
A.1.9 Unknown Collisional Cross-Sections
A.1.10
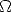 -Fit of 3rd Degree
-Fit of 3rd Degree
A.1.11 Mg I: Allowed Transitions from its Ground State
A.1.12 van-Regemorter: Combined Levels of Complex Ions
A.1.21 He II: Transition between its Levels with s < 4
A.1.25
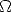 -Fit in Temperature, General Case
-Fit in Temperature, General Case
A.1.26
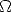 -Fit in log T, General Case
-Fit in log T, General Case
A.2 CBF Transitions
A.2.1 Hydrogen, n = 1,..., 10
A.2.2 He I, n = 1,..., 10
A.2.3 He II, n < 15
A.2.4 Seaton Formula
A.2.5 Lotz Formula
A.2.6 Mg I 3s
 Mg I 2p6 +
Mg I 2p6 + 
A.3 RBB Transitions
A.3.1 Doppler Profiles
A.3.2 Voigt Profiles, only Radiative Damping
A.3.3 Voigt Profiles, Radiative and Collisional Damping (Electrons)
A.3.4 Voigt Profiles and “Stark Wings” (Linear Stark Effect)
A.3.5 Stark Line Broadening following Dimitrijévic
A.4 RBF Transitions
A.4.1 Seaton Formula
A.4.2 Seaton Formula with Gaunt Factor
A.4.3 Koester Formula for He III
A.4.4 Opacity-Project Photoionization Cross-Sections, Seaton tails
A.4.5 Karzas & Latter data with Gaunt Factor
A.4.10 Opacity-Project Photoionization Cross-Sections
A.4.12 DETAIL Fit Formula
A.5 RFF Transitions
A.5.1 Including Contributions of LTE Levels (Unsöld)
A.5.2 Including Contributions of LTE Levels with Gaunt Factors
A.5.3 With Gaunt Factors, no LTE Contributions
B Fundamental Constants
C Solar Abundances
D How to calculate a NLTE model with TMAP
D.1 Basics
D.2 Creation of atomic data files with ATOMS2
D.3 Creation of a frequency grid with SETF2
D.4 Adaption of the Parameter files
D.5 Calculation of a start model with LTE2
D.6 Calculation of a NLTE model with PRO2
D.7 Strategy to calculate a NLTE model with PRO2
D.8 Example: A model with hydrogen and helium
D.8.1 ATOMS2
D.8.2 SETF2
D.8.3 Parameter files
D.8.4 LTE2
D.8.5 PRO2
D.9 Naming the TMAP models
E Colors
F References